Abstract: A brand new research reveals that the Mediterranean weight-reduction plan might improve cognitive operate by altering intestine microbiota. Rats fed a Mediterranean-style weight-reduction plan confirmed distinct bacterial modifications linked to raised reminiscence, cognitive flexibility, and dealing reminiscence in comparison with these on a Western weight-reduction plan.
Helpful micro organism ranges elevated, whereas dangerous ones decreased, bettering efficiency on reminiscence and studying duties. These findings recommend that dietary patterns affect mind well being by the intestine, doubtlessly benefiting younger adults throughout essential developmental intervals.
Key Information:
- Intestine-Mind Connection: The Mediterranean weight-reduction plan reshapes intestine microbiota, bettering cognitive operate.
- Cognitive Good points: Higher reminiscence, flexibility, and dealing reminiscence had been linked to intestine micro organism modifications.
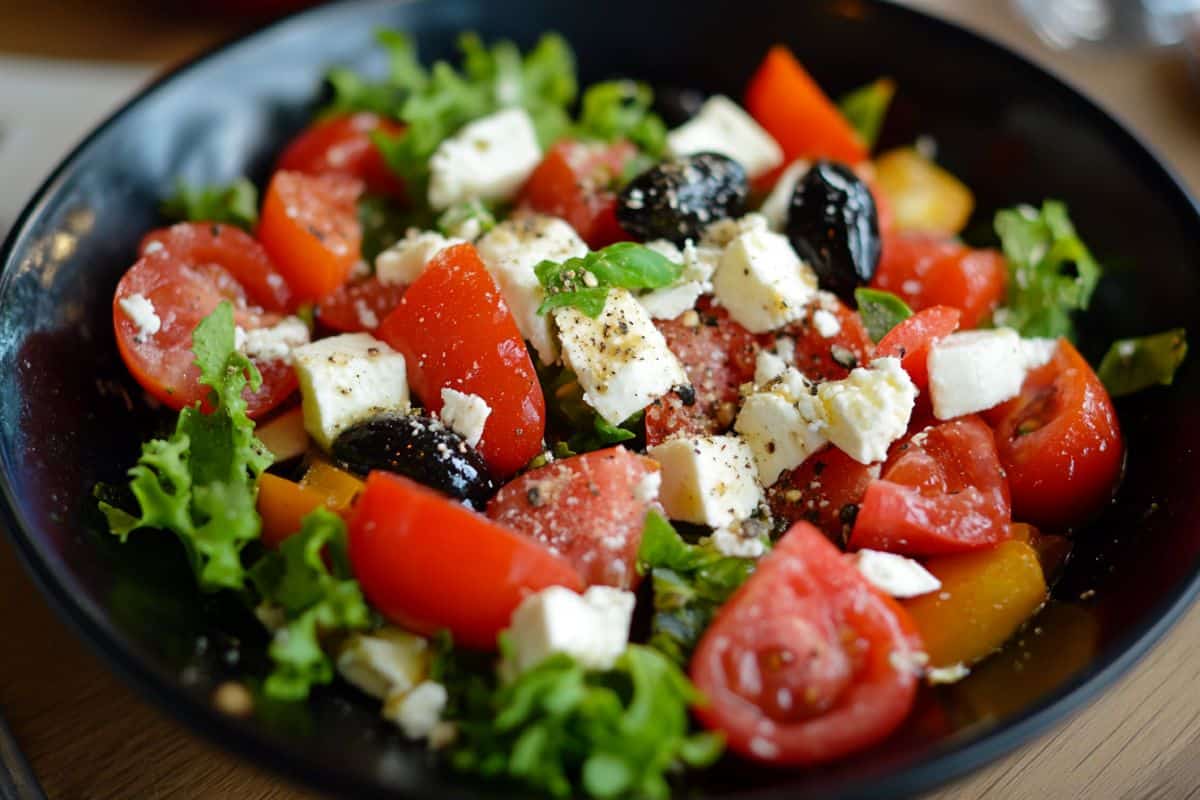
- Dietary Influence: Mediterranean elements like olive oil, fish, and fiber boosted useful micro organism.
Supply: Tulane College
A brand new Tulane College research suggests the Mediterranean weight-reduction plan’s brain-boosting advantages may go by altering the steadiness of micro organism within the intestine.
In a research printed in Intestine Microbes Stories, researchers at Tulane College College of Drugs discovered that topics following a Mediterranean weight-reduction plan developed distinctly totally different intestine micro organism patterns in comparison with these consuming a typical Western weight-reduction plan.
These bacterial modifications correlated with higher reminiscence and cognitive efficiency.

“We’ve identified that what we eat impacts mind operate, however this research explores how that may very well be occurring,” mentioned lead creator Rebecca Solch-Ottaiano, PhD, neurology analysis teacher at Tulane’s Medical Neuroscience Analysis Heart.
“Our findings recommend that dietary selections can affect cognitive efficiency by reshaping the intestine microbiome.”
The research discovered that rats fed a Mediterranean-style weight-reduction plan wealthy in olive oil, fish and fiber over 14 weeks confirmed will increase in 4 useful varieties of intestine micro organism and reduces in 5 others in comparison with rats consuming a Western weight-reduction plan excessive in saturated fat.
These bacterial modifications had been linked to improved efficiency on maze challenges designed to check reminiscence and studying.
Particularly, greater ranges of micro organism resembling Candidatus Saccharimonas had been related to higher cognitive efficiency, whereas elevated ranges of different micro organism, resembling Bifidobacterium, correlated with poorer reminiscence operate.
The Mediterranean weight-reduction plan group additionally confirmed higher cognitive flexibility — the flexibility to adapt to new info — and improved working reminiscence in comparison with the Western weight-reduction plan group. They maintained decrease ranges of “dangerous” LDL ldl cholesterol.
This research is the primary to evaluate the results of the Mediterranean on microbiota and cognitive operate outcomes relative to the Western weight-reduction plan in a rodent mannequin. The researchers used younger rats roughly equal in age to 18-year-old people to mannequin the results of weight-reduction plan throughout a essential developmental interval.
The diets had been primarily based on human consumption and used substances reflecting the complexity of human diets. The Mediterranean weight-reduction plan (MeDi) confirmed clear advantages for cognitive flexibility, reminiscence, and intestine well being, suggesting potential parallels in younger adults whose brains and our bodies are nonetheless maturing.
“Our findings recommend that the Mediterranean weight-reduction plan or its organic results may very well be harnessed to enhance scholastic efficiency in adolescents, or work efficiency in younger adults,” mentioned corresponding creator Dr. Demetrius M. Maraganore, Herbert J. Harvey, Jr. Chair of Neurosciences.
“Whereas these findings are primarily based on animal fashions, they echo human research linking the Mediterranean weight-reduction plan to improved reminiscence and diminished dementia danger.”
The researchers emphasize that bigger human research are wanted to substantiate these results and higher perceive the complicated relationship between weight-reduction plan, intestine micro organism, and mind operate in younger individuals.
For these keen on following a Mediterranean consuming sample, key elements embody:
– Olive oil as the first fats supply
– Plentiful greens, fruits and complete grains
– Fish and lean proteins
– Restricted crimson meat and saturated fat
– Excessive fiber consumption from numerous plant sources
Different Tulane co-authors of the research embody Elizabeth B. Engler-Chiurazzi, Colin Harper, Savannah Wasson, Sharon Ogbonna, Blake Ouvrier, Hanyun Wang, Madison Prats, Katherine McDonald, Ifechukwude J. Biose, Lori A. Rowe, MaryJane Jones, Chad Steele and Gregory Bix.
About this weight-reduction plan and cognition analysis information
Creator: Keith Brannon
Supply: Tulane College
Contact: Keith Brannon – Tulane College
Picture: The picture is credited to Neuroscience Information
Unique Analysis: Open entry.
“Comparability between two divergent diets, Mediterranean and Western, on intestine microbiota and cognitive operate in younger sprague dawley rats” by Rebecca Solch-Ottaiano et al. Intestine Microbes Stories
Summary
Comparability between two divergent diets, Mediterranean and Western, on intestine microbiota and cognitive operate in younger sprague dawley rats
Medical research strongly recommend the significance of weight-reduction plan high quality on cognition in youth populations (15–24 years).
The Mediterranean weight-reduction plan (MeDi) has been proven to enhance cognition in distinction to the generally consumed Western weight-reduction plan (WD). The intestine microbiota might function a mechanism for diet-induced modifications in cognition.
Ten-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats had been assigned a MeDi or WD (n = 10/group) for 14 weeks. Previous to neurobehavior assessments, microbiota neighborhood composition was assessed.
On the genus stage, the relative abundance of 4 micro organism elevated with the MeDi and 5 decreased in comparison with the WD. Rats within the MeDi group demonstrated cognitive flexibility and enchancment in reference and dealing reminiscence relative to the WD group.
On the finish of the research, serum cytokines had been elevated, and low-density lipoproteins had been decreased within the MeDi group. Markers for neuroinflammation, blood-brain barrier, glial cells, and synaptic plasticity in mind areas didn’t differ between teams.
General, the MeDi modulated intestine microbiota, cognitive operate, and serum lipid and cytokines however not gene expression within the mind in comparison with the WD.
Additional research are wanted to find out causality between diet-modulated intestine microbiota, cognitive operate, and immune operate.














Discussion about this post