Abstract: By analyzing fMRI scans of individuals watching movies, neuroscientists have created a complete useful map of the mind, exhibiting the way it prompts in response to complicated scenes. This research recognized 24 distinct networks that course of facets like faces, speech, or motion, and revealed how government capabilities shift between simple and difficult scenes.
Utilizing machine studying on information from the Human Connectome Challenge, the analysis mapped areas that reply to various audio-visual stimuli. The findings might inform future research on how particular person mind responses differ with age or cognitive problems.
Key Information:
- Scanning brains throughout film watching highlighted 24 networks for particular processing, like social interactions and object recognition.
- Complicated scenes activate government management areas, whereas less complicated scenes activate language or sensory areas.
- That is the primary detailed useful map created beneath naturalistic circumstances utilizing various movie clips.
Supply: Cell Press
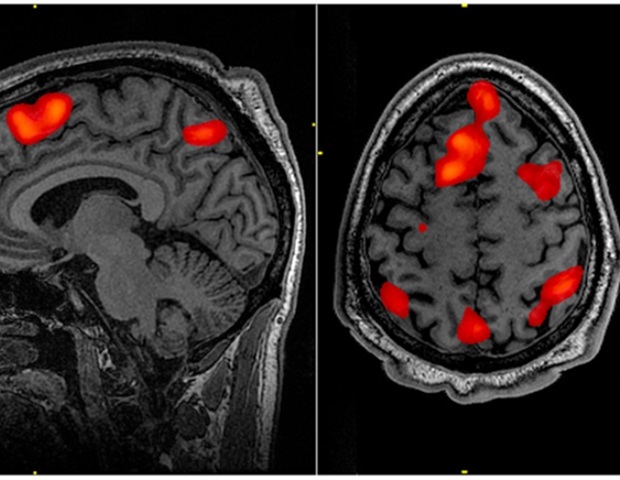
By scanning the brains of individuals whereas they watched film clips, neuroscientists have created probably the most detailed useful map of the mind so far.
The fMRI evaluation, publishing November 6 within the Cell Press journal Neuron, exhibits how completely different mind networks mild up when contributors seen brief clips from a spread of unbiased and Hollywood movies together with Inception, The Social Community, and Dwelling Alone.

The workforce recognized completely different mind networks concerned in processing scenes with folks, inanimate objects, motion, and dialogue. Additionally they revealed how completely different government networks are prioritized throughout easy- versus hard-to-follow scenes.
“Our work is the primary try and get a format of various areas and networks of the mind throughout naturalistic circumstances,” says first writer and neuroscientist Reza Rajimehr of Massachusetts Institute of Expertise (MIT).
Totally different areas of the mind are extremely interconnected, and these connections type useful networks that relate to how we understand stimuli and behave. Most research of mind useful networks have been primarily based on fMRI scans of individuals at relaxation, however many elements of the mind or cortex aren’t totally energetic within the absence of exterior stimulation.
On this research, the researchers wished to research whether or not screening films throughout fMRI scanning might present perception into how the mind’s useful networks reply to complicated audio and visible stimuli.
“With resting-state fMRI, there isn’t any stimulus—persons are simply considering internally, so that you don’t know what has activated these networks,” says Rajimehr.
“However with our film stimulus, we will return and determine how completely different mind networks are responding to completely different facets of the film.”
To map the mind throughout film watching, the researchers leveraged a beforehand collected fMRI dataset from the Human Connectome Challenge, consisting of complete mind scans from 176 younger adults that have been obtained whereas the contributors watched 60 minutes’ value of brief clips from a spread of unbiased and Hollywood movies.
The researchers averaged the mind exercise throughout all contributors and used machine studying methods to determine mind networks, particularly throughout the cerebral cortex. Then, they examined how exercise inside these completely different networks associated to the film’s scene-by-scene content material—which included folks, animals, objects, music, speech, and narrative.
Their evaluation revealed 24 completely different mind networks that have been related to particular facets of sensory or cognitive processing, for instance recognizing human faces or our bodies, motion, locations and landmarks, interactions between people and inanimate objects, speech, and social interactions.
Additionally they confirmed an inverse relationship between “government management domains”—mind areas that allow folks to plan, clear up issues, and prioritize info—and mind areas with extra particular capabilities.
When the film’s content material was tough to comply with or ambiguous, there was heightened exercise in government management mind areas, however throughout extra simply comprehendible scenes, mind areas with particular capabilities, like language processing, predominated.
“Govt management domains are often energetic in tough duties when the cognitive load is excessive,” says Rajimehr.
“It seems to be like when the film scenes are fairly simply comprehendible, for instance if there’s a transparent dialog occurring, the language areas are energetic, however in conditions the place there’s a complicated scene involving context, semantics, and ambiguity within the which means of the scene, extra cognitive effort is required, and so the mind switches over to utilizing basic government management domains.”
For the reason that analyses on this paper have been primarily based on common mind actions, the researchers say that future analysis might examine how mind community perform differs between people, between people of various ages, or between people with developmental or psychiatric problems.
“In future research, we will take a look at the maps of particular person topics, which might enable us to narrate the individualized map of every topic to the behavioral profile of that topic,” says Rajimehr.
“Now, we’re finding out in additional depth how particular content material in every film body drives these networks—for instance, the semantic and social context, or the connection between folks and the background scene.”
Funding:
This analysis was supported by the McGovern Institute for Mind Analysis, the Cognitive Science and Expertise Council of Iran, the MRC Cognition and Mind Sciences Unit, and a Cambridge Belief scholarship.
About this mind mapping analysis information
Creator: Kristopher Benke
Supply: Cell Press
Contact: Kristopher Benke – Cell Press
Picture: The picture is credited to Neuroscience Information
Authentic Analysis: Open entry.
“Purposeful structure of cerebral cortex throughout naturalistic movie-watching” by Reza Rajimehr et al. Neuron
Summary
Purposeful structure of cerebral cortex throughout naturalistic movie-watching
Characterizing the useful group of cerebral cortex is a elementary step in understanding how completely different varieties of data are processed within the mind. Nonetheless, it’s nonetheless unclear how these areas are organized throughout naturalistic visible and auditory stimulation.
Right here, we used high-resolution useful MRI information from 176 human topics to map the macro-architecture of your entire cerebral cortex primarily based on responses to a 60-min audiovisual film stimulus.
A knowledge-driven clustering method revealed a map of 24 useful areas/networks, every explicitly linked to a particular facet of sensory or cognitive processing.
Novel options of this map included an prolonged scene-selective community within the lateral prefrontal cortex, separate clusters attentive to human-object and human-human interplay, and a push-pull interplay between three government management (domain-general) networks and domain-specific areas of the visible, auditory, and language cortex.
Our cortical parcellation supplies a complete and unified map of functionally outlined areas within the human cerebral cortex.


















Discussion about this post