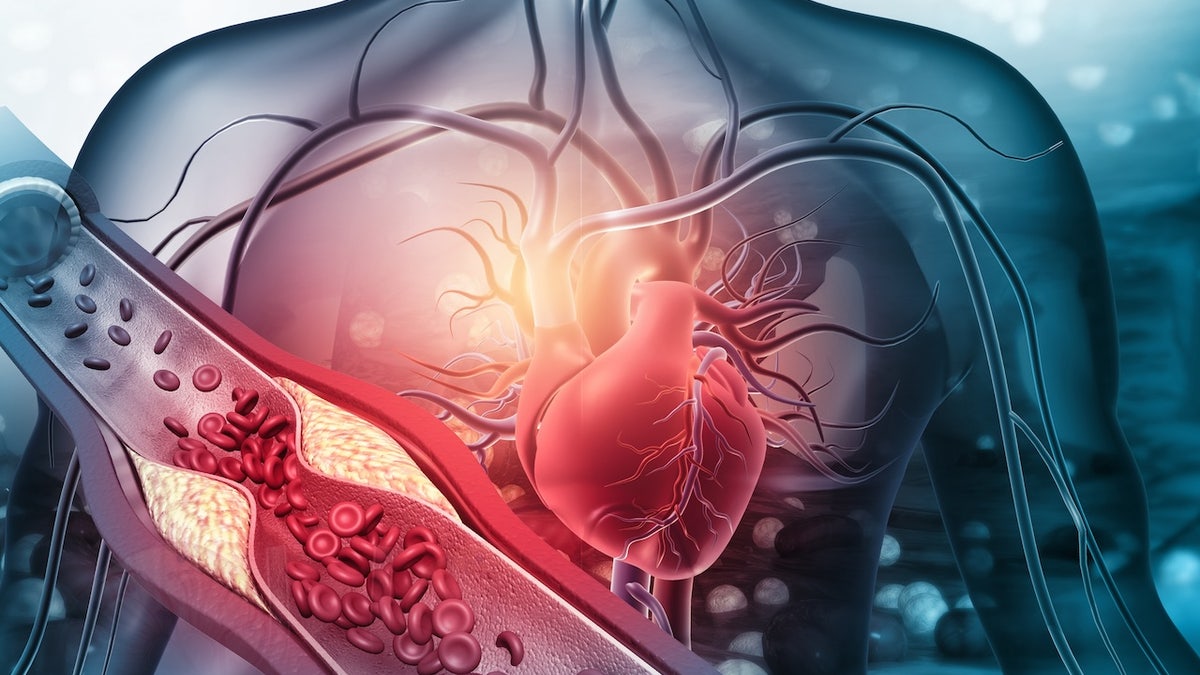
Heart disease is the main cause of mortality of the world, which contains 32% of all deaths.
But that doesn’t mean that people are powerless against the condition – there are some steps they can do to help reduce the risk.
In addition to adopt healthier ways of life, obtaining a specific screening – the coronary arterial calcium (CAC) – can help detect early signs of heart disease, say experts.
Disease starts on your plate, cardiologist says – that’s what to change
What is the CAC score?
The CAC score is a specialized CT scan, which measures calcium construction in the walls of the heart arteries, according to board-certified cardiologist Dr. Robert Segal, founder of Manhattan Cardiology and co-founder of https://www.labinder.com.
Get a specific screening – the coronary arterial calcium (CAC) score – can help detect early signs of heart disease, say experts. (istock)
“This calcium notes the accumulation of plaque that can cause heart disease,” he told Fox News Digital.
The higher the score, the more calcium in the arteries, so greater probability of a heart attack, stroke or other heart affair.
Some winter viruses could trigger heart complications, experts warn
Calcium score of zero indicates no coronary calcium and places the individual at a very low risk for heart disease. Calcium -score greater than 400 indicates a high risk of heart disease, according to Dr. Bradley Serwer, an intervention cardiologist and chief physician at Vitalsolation, an Ingenov -health company that offers cardiovascular and anesthesiological services to hospitals.
“The CAC score is acquired by a fast, low-dose CT scan,” a Maryland-based server told Fox News Digital.
“High score indicates that you need to work with your doctor to reduce your risk.”
The scan images are processed with specialized computer software, producing what is called an “Agatston score.”
“This computer algorithm estimates how much calcium is present and calculates a number or score,” Serwer said.
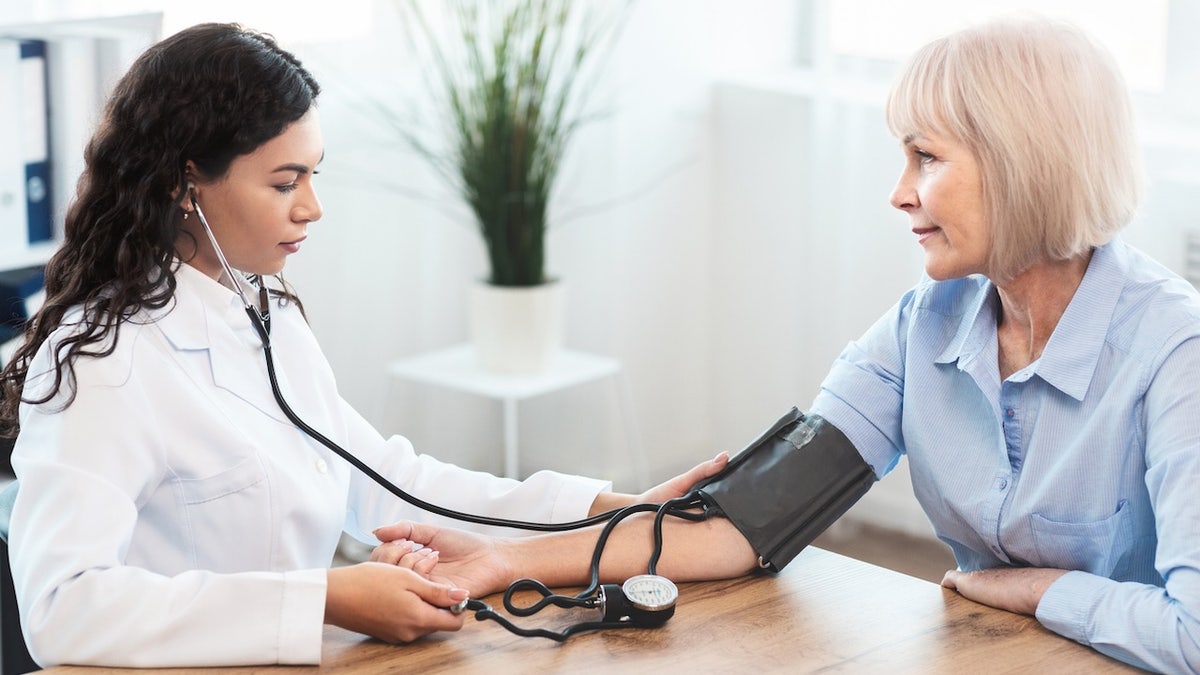

The CAC score is a “non-traditional risk factor”, which is not as widely known as more routine projects as cholesterol checks or blood pressure, according to one expert. (istock)
The CAC score is a “non-traditional risk factor”, which is not as widely known as more routine projects as cholesterol checks or blood pressure, according to Segal.
“However, awareness increases, as more research shows how valuable it is to predict a heart disease,” he said.
What to do with the CAC score
The result of the scan can help people commission their heart conditions, says experts.
“It’s helpful because it helps to identify heart disease early, even if you don’t have symptoms,” Segal said. “This allows preventive steps, such as lifestyle changes or medications, to lower your risk.”
Click here to register for our health information
If the CAC score is zero, Segal recommends maintaining good practices and continue to track risky variables.
“Low score indicates a gentle plate; hence lifestyle changes like improving a diet, exercising and lowering cholesterol will help,” he said. “High score indicates that you need to work with your doctor to reduce your risk, maybe with statins.”
The result of the scan helps people detect and commission their heart conditions even if they do not have symptoms, say experts. (istock)
In general, if CAC score is zero, there is little need to repeat the study for five years, according to Serwer.
For those with raised calcium score, there are limited data on the benefit of repeat tests.
“These patients must discuss their individual case with a trained cardiologist to determine the need for further testing,” Serwer advised.
This disease kills more people than all cancers and accidents combined
The test is used in combination with other risk factors, such as cholesterol, blood pressure and diabetes, to determine who needs aggressive medical therapy for primary prevention of heart disease.
“The sooner we can identify those with a higher risk of a heart attack, the sooner we can start them with tested therapies to avoid bad results,” Serwer said.
“While we don’t have data that shows just performing this test, make you live longer, knowing who we need to treat aggressively and know when we can delay or avoid medical therapy is very important.”
Possible risks and restrictions
As for possible risk, Segal compared the CAC scan to mammography, noting that it is fast, uninvasive, uses only a small radiation, and does not involve dye injection.
“It just measures current calcium, and it can’t identify a soft plaque not consolidated,” he noted.
The test can be done in most radiological departments. For those who only get a coronary arterial pottery score, there is no need for preparation. (istock)
Segal also warned that zero CAC score does not imply zero risk – especially in cases of diabetes or smoking, which are additional risk factors.
“It is a useful instrument to be joined with other health assessments,” he added.
How to get the test
People interested in the CAC score must start seeing a cardiologist.
“Those between 40 and 70 years old, who have risky factors such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure or family history of heart disease usually advises to get the scan,” Segal said.
Click here to get the Fox News app
Serwer recommends that patients discuss individual risk with their primary caregiver to determine if the test will be helpful.
“We do not currently have standardized guidelines for testing or frequency of repeated tests,” he said.
“Some plans consider this test election or research test and will therefore not be paid for it.”
The test can be done in most radiological departments. For those who only receive a coronary arterial calcium score, there is no need for preparation, a server noted.
“There is no need for an IV contrast, so there is no need to fast or get blood work before getting this study.”
Coverage for the CAC test varies based on individual insurance plans.
For more health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“Some plans consider this test election or research test and will therefore not be paid for it,” Serwer noted.
“Medicare currently does not cover the cost for asymptomatic people for risky stratification purposes.”