Abstract: Researchers have developed a machine studying mannequin that upgrades 3T MRI pictures to imitate the higher-resolution 7T MRI, offering enhanced element for detecting mind abnormalities. The artificial 7T pictures reveal finer options, corresponding to white matter lesions and subcortical microbleeds, which are sometimes tough to see with normal MRI methods.
This AI-driven method might enhance diagnostic accuracy for situations like traumatic mind injury (TBI) and a number of sclerosis (MS), although medical validation is required earlier than wider use. The brand new mannequin might in the end develop entry to high-quality imaging insights with no need specialised tools. This development marks a promising intersection of AI and medical imaging expertise.
Key Details
- AI mannequin enhances 3T MRIs to intently approximate the element of 7T MRIs.
- Artificial 7T pictures confirmed sharper mind lesion boundaries, aiding analysis.
- Mannequin may benefit TBI and MS sufferers by bettering visualization of mind abnormalities.
Supply: UCSF
On the intersection of AI and medical science, there may be rising curiosity in utilizing machine studying to reinforce imaging knowledge captured by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) expertise.
Current research present that ultra-high-field MRI at 7 Tesla (7T) might have far better decision and medical benefits over high-field MRI at 3T in delineating anatomical buildings which are essential for figuring out and monitoring pathological tissue, notably within the mind.
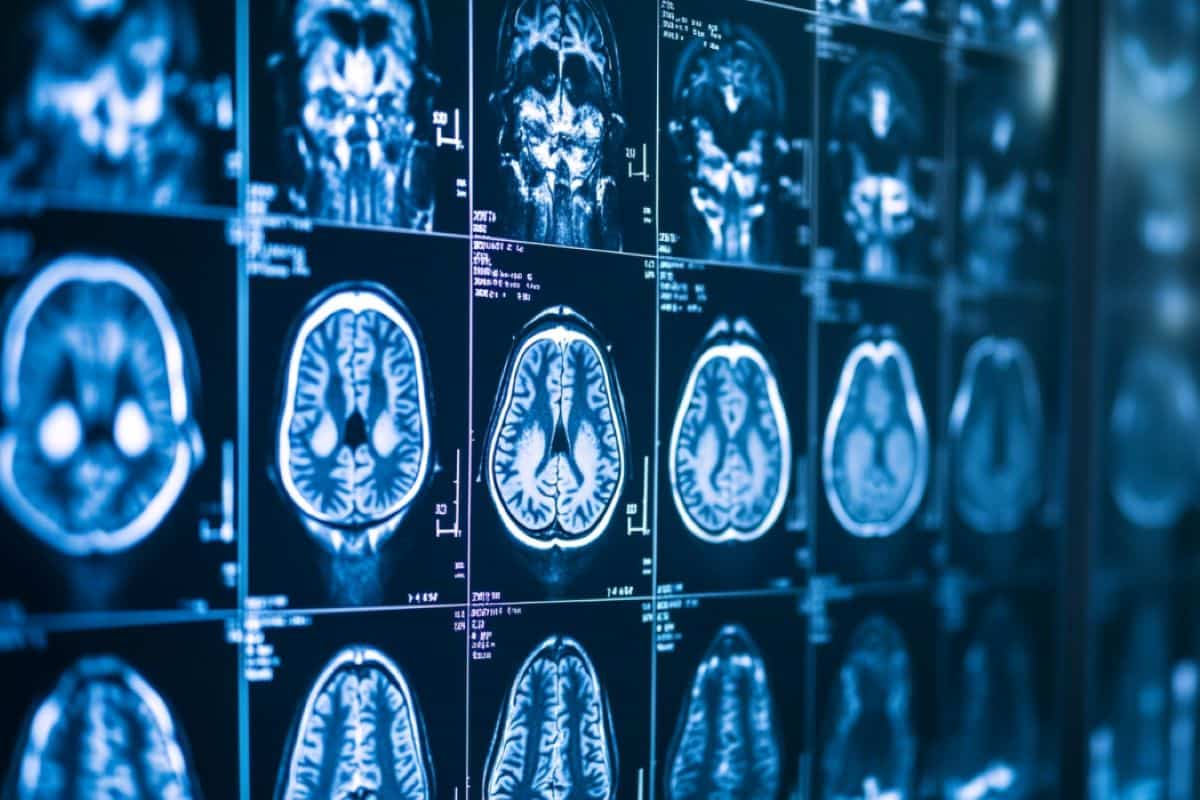
Most medical MRI exams within the U.S. are carried out with 1.5T or 3T MRI methods. As lately as 2022, the Nationwide Institutes of Health documented solely about 100 7T MRI machines getting used for diagnostic imaging worldwide.
Researchers from UC San Francisco developed a machine studying algorithm to reinforce 3T MRIs by synthesizing 7T-like pictures that approximate actual 7T MRIs.
Their mannequin enhanced pathological tissue with extra constancy for medical insights and represents a brand new step towards evaluating medical purposes of artificial 7T MRI fashions.
The examine was introduced Oct. 7 on the twenty seventh Worldwide Convention on Medical Picture Computing and Laptop Assisted Intervention (MICCAI).
“Our paper introduces a machine-learning mannequin to synthesize high-quality MRIs from lower-quality pictures. We exhibit how this AI system improves the visualization and identification of mind abnormalities captured by MRIs in Traumatic Mind Damage,” mentioned senior examine creator Reza Abbasi-Asl, Ph.D., UCSF Assistant Professor of Neurology.
“Our findings spotlight the promise of AI and machine studying to enhance the standard of medical pictures captured by much less superior imaging methods.”
Higher to see TBI and a number of sclerosis with
UCSF researchers collected imaging knowledge from sufferers recognized with delicate traumatic mind injury (TBI) at UCSF. They designed and skilled three neural community fashions to carry out picture enhancement and 3D picture segmentation utilizing the generated synthetic-7T MRIs from the usual 3T MRIs.
The pictures generated with the brand new fashions supplied enhanced pathological tissue for sufferers with delicate TBI. They chose an instance area with white matter lesions and microbleeds in subcortical areas to make use of for comparability.
They discovered pathological tissue was simpler to see in synthesized 7T pictures. This was evident within the separation of adjoining lesions and the sharper contours of subcortical microbleeds.
Moreover, the synthesized 7T pictures higher captured the varied options inside white matter lesions. These observations additionally spotlight the promise of utilizing this expertise to enhance diagnostic accuracy in neurodegenerative issues corresponding to a number of sclerosis.
Whereas synthetization methods based mostly on machine studying frameworks exhibit outstanding efficiency, their software in medical settings would require in depth validation.
The researchers consider that future work ought to embody in depth medical evaluation of the mannequin findings, medical score of model-generated pictures, and quantification of uncertainties within the mannequin.
About this AI and neuroimaging analysis information
Creator: Reza Abbasi-Asl
Supply: UCSF
Contact: Reza Abbasi-Asl – UCSF
Picture: The picture is credited to Neuroscience Information



















Discussion about this post