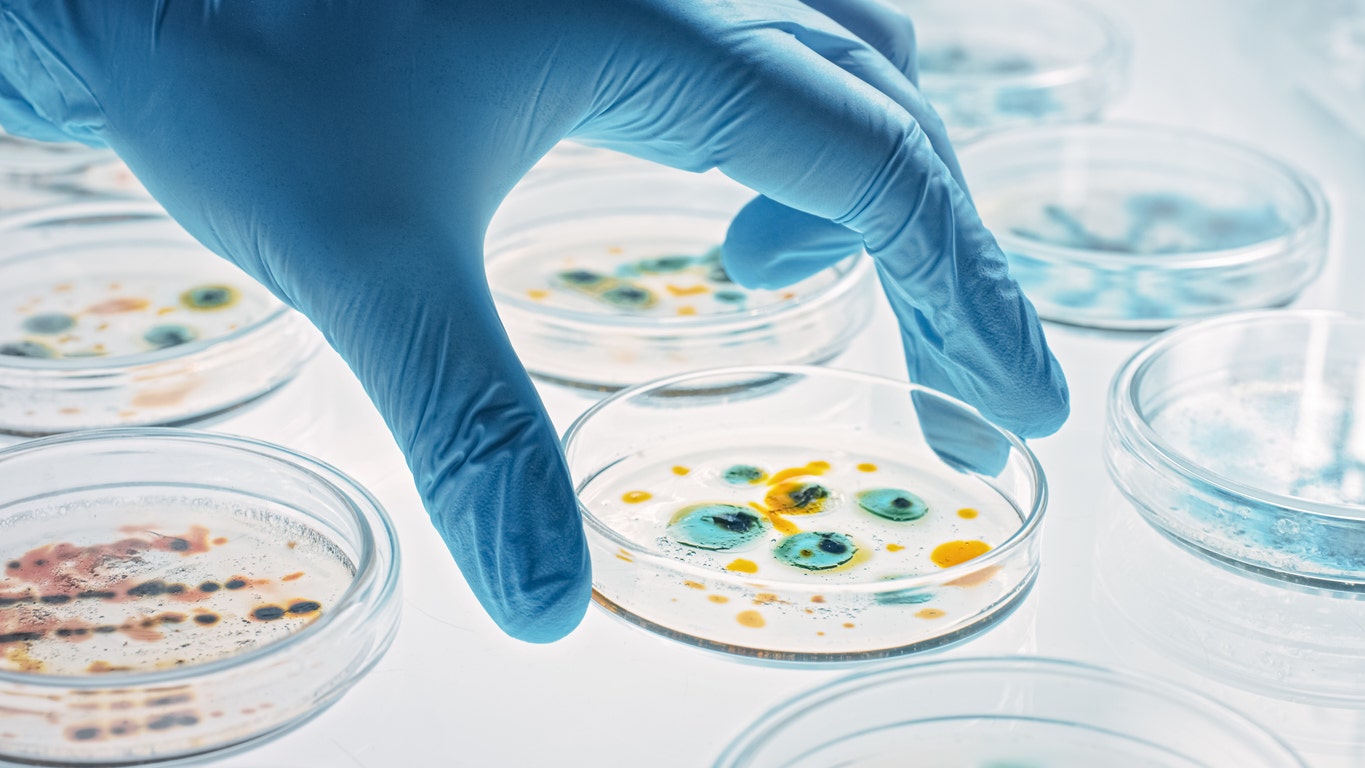
Resistance to antibiotics has led to 1 million worldwide deaths every year since 1990, for a complete of 36 million.
It’s anticipated to trigger greater than 39 million extra fatalities by 2050 — three per minute.
That’s in response to a big examine led by the International Analysis on Antimicrobial Resistance (GRAM) Venture, a partnership between the College of Oxford and the Institute for Health Metrics and Analysis (IHME) on the College of Washington.
NEW ANTIBIOTIC KILLS DEADLY, DRUG-RESISTANT BACTERIA IN ‘SCIENTIFIC BREAKTHROUGH’
After analyzing 520 million well being information, the researchers offered future estimates for 22 pathogens, 84 pathogen-drug combos and 11 infectious syndromes throughout 204 international locations and territories, in response to a GRAM press launch.
Resistance to antibiotics has led to 1 million worldwide deaths every year since 1990, for a complete of 36 million. (iStock)
Findings from the examine have been revealed in The Lancet on Monday.
What’s antimicrobial resistance?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) happens when micro organism and different varieties of germs turn into stronger than the drugs given to deal with them, creating so-called “superbugs.”
This will make infections troublesome or not possible to deal with, per the U.S. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention (CDC).
WHY ANTIBIOTICS MAY NOT HELP PATIENTS SURVIVE THEIR VIRAL INFECTIONS: NEW RESEARCH
“In trendy medication, the usage of antibiotics has allowed us to efficiently carry out organ transplants, complicated surgical procedures and care for very preterm infants,” Jasmine Riviere Marcelin, MD, a fellow of the Infectious Illnesses Society of America and infectious illnesses professor on the College of Nebraska — who was not concerned within the examine — instructed Fox Information Digital.
“These interventions have been profitable as a result of antibiotics have allowed us to stop and deal with infections in these critically unwell sufferers.”
Antimicrobial resistance happens when micro organism and different varieties of germs turn into stronger than the drugs given to deal with them, creating so-called “superbugs.” (iStock)
Now, antibiotic-resistant micro organism pose a “vital well being danger,” she warned, as a result of they forestall the power to deal with or forestall infections.
“Not solely will our developments in medication be in danger, however we could discover ourselves again to the place we have been within the pre-antibiotic period, when mortality from easy pores and skin/comfortable tissue infections was vital,” Marcelin added.
“We could discover ourselves again to the place we have been within the pre-antibiotic period.”
Maureen Tierney, MD, affiliate dean of medical analysis and public well being at Creighton College Faculty of Medication in Omaha, Nebraska, was additionally not concerned within the examine, however confirmed that it’s “essentially the most complete try to find out the burden of antimicrobial resistance [in terms of] incapacity and demise.”
“This was an infinite effort utilizing all totally different sources of information in international locations world wide to estimate the variety of deaths brought on by microorganisms immune to a number of varieties of antibiotics,” she instructed Fox Information Digital.
Marking key shifts
Since 1990, the an infection that brought on the most important enhance was MRSA (methicillin-resistant S. aureus), a kind of staph micro organism that has turn into immune to some antibiotics.
Annual MRSA-related deaths elevated from 57,200 in 1990 to 130,000 in 2021, the examine discovered.
Regardless of the general enhance in AMR-related mortality, deaths amongst children youthful than 5 have been reduce in half between 1990 and 2021.
Since 1990, the an infection that brought on the most important enhance was MRSA (methicillin-resistant S. aureus), a kind of staph micro organism that has turn into immune to some antibiotics. (iStock)
The researchers attributed this to childhood vaccination packages and wider entry to consuming water, sanitation and hygiene practices.
The sharpest enhance was amongst adults 70 and older, who noticed a greater than 80% uptick in AMR deaths.
‘VACCINE FATIGUE’ BLAMED AS ROUGHLY HALF OF PEOPLE IN US WILL SKIP COVID AND FLU SHOTS THIS YEAR
“Researchers count on these tendencies to proceed within the coming many years, with AMR deaths amongst kids beneath 5 projected to halve by 2050 globally, as deaths amongst individuals 70 years and older greater than double,” the press launch said.
Geographically, deaths rose essentially the most in western sub-Saharan Africa, tropical Latin America, high-income North America, Southeast Asia and South Asia.
Combating antimicrobial resistance
Subsequent week, international well being leaders plan to fulfill on the UN Basic Meeting in New York to debate new methods for addressing AMR.
Potential interventions embrace “an infection prevention and management measures, reminiscent of new vaccines and antimicrobials, and improved entry to water and sanitation — in addition to deeper investments throughout well being methods in diagnostics, coaching and new applied sciences,” the discharge said.
“Crucial methods to lower the incidence of antibiotic resistance are vaccination for pneumonia, influenza, COVID, measles and different illnesses,” an infectious illnesses skilled instructed Fox Information Digital. (Jeff Kowalsky/AFP through Getty Photographs))
“Crucial methods to lower the incidence of antibiotic resistance are vaccination for pneumonia, influenza, COVID, measles and different illnesses,” Tierney from Creighton College instructed Fox Information Digital.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Tierney additionally requires “antimicrobial stewardship” – which she defines as “the even handed use of antibiotics in people, animals and farming” – in addition to an infection prevention practices, particularly in well being care services, and the event of recent antibiotics.
“Antibiotics are a shared pure useful resource that we should all shield.”
Whereas creating new medication is one technique to fight AMR, Marcelin warned that relying solely on drug discovery can be “futile,” given the size of time it takes for brand spanking new drugs to be developed, examined and accredited.
“The variety of new or repurposed antibiotics in late-stage medical improvement may be very small, and no single antibiotic candidate claims to have exercise in opposition to these micro organism immune to all presently out there medication,” she instructed Fox Information Digital.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“If we are able to’t make new medication simply, we are able to fight resistance by controlling the unfold of resistant organisms, which is the precept of an infection management.”
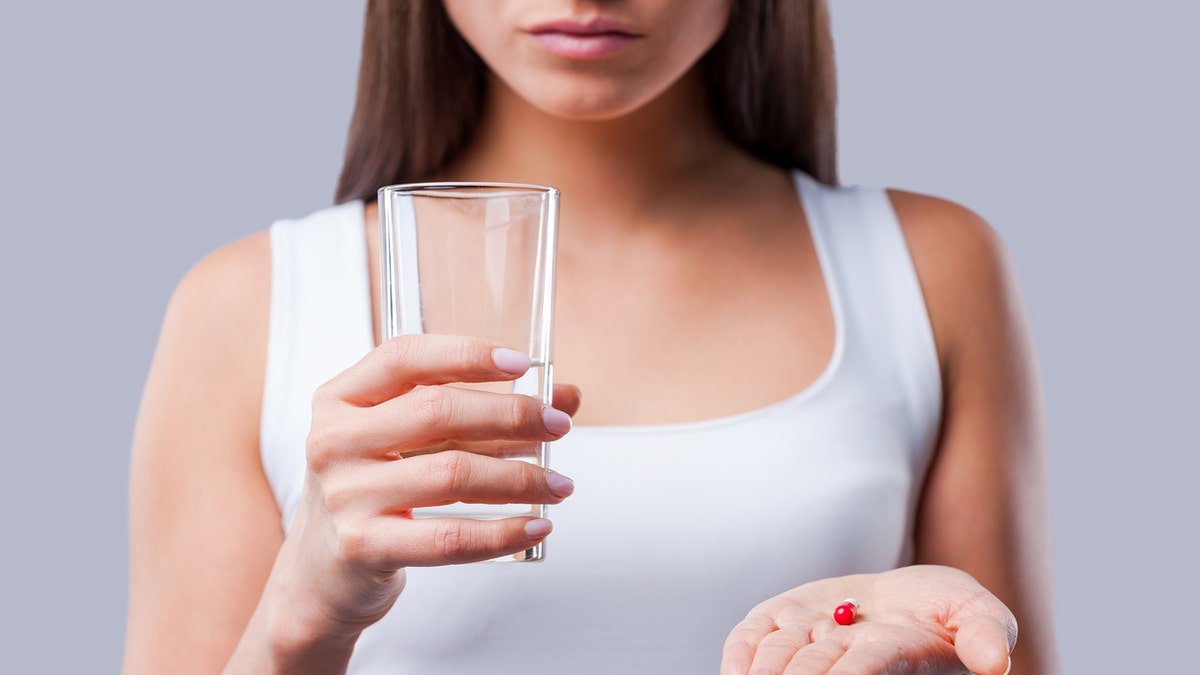

To stop resistance, consultants say that antibiotics needs to be prescribed and used “solely when they’re indicated, for the optimum period, and on the proper timing and dosing routine.” (iStock)
To stop resistance, Marcelin agrees that antibiotics needs to be prescribed and used “solely when they’re indicated, for the optimum period, and on the proper timing and dosing routine.”
She added, “Antibiotics are a shared pure useful resource that we should all shield, in order that we are able to proceed to reside in a world the place we make medical advances and cut back mortality from bacterial infections.”
For extra Health articles, go to www.foxnews.com/well being
Fox Information Digital reached out to GRAM researchers requesting remark.














Discussion about this post