Abstract: Researchers found how the protein CGRP impacts the mind’s lymphatic system, contributing to migraine ache. Their research reveals that CGRP prevents cerebrospinal fluid from draining, influencing migraine assaults.
This discovering might result in new therapeutic methods for migraines. Extra analysis is required to grasp the intercourse variations in migraine prevalence.
Key Information:
- CGRP influences lymphatic vessels, stopping cerebrospinal fluid drainage and contributing to migraine ache.
- Mouse fashions resistant to CGRP results skilled much less migraine-related ache.
- Future research intention to discover the connection between migraines, CGRP, and the mind’s lymphatic system.
Supply: UNC
Migraine is a persistent and debilitating neurological situation affecting girls 3 to 4 extra instances than males. Regardless of an estimated 1.1 billion individuals being impacted by the situation, the physiological underpinnings of migraine stay mysterious, however are extremely studied.
For the primary time, researchers from the UNC College of Drugs’s Division of Cell Biology and Physiology have pieced collectively how a small protein referred to as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) influences the lymphatic vascular system, contributing to the ache throughout migraine assaults.

Their outcomes had been printed within the Journal of Medical Investigation.
“Our research has highlighted the significance of the mind’s lymphatic system within the pathophysiology of migraine ache,” mentioned Kathleen M. Caron, PhD, the Frederick L. Eldridge Distinguished Professor and chair of the Division of Cell Biology and Physiology and senior writer on the research.
“We discovered that migraine ache is influenced by altered interactions with immune cells and by CGRP stopping cerebrospinal fluid from draining out of the meningeal lymphatic vessels.”
CGRP, a small protein that’s sometimes concerned in ache transmission in neurons, is understood to be elevated within the meninges, or the layers of tissues surrounding the mind, throughout migraine assaults.
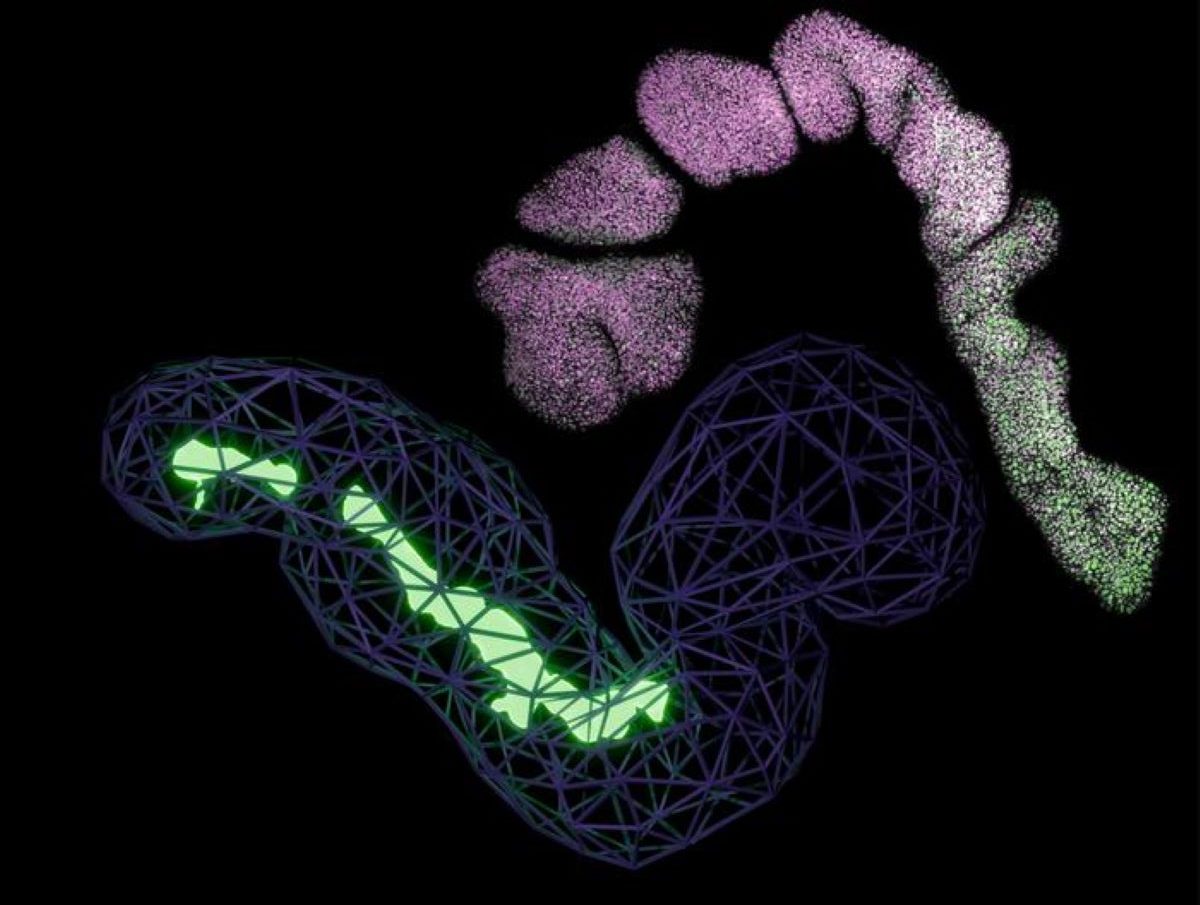
The group found that will increase in CGRP ranges additionally has a profound impact on the mind’s lymphatic vessels – a particular system that facilitates the elimination of cerebrospinal fluid and creates pathways for immune cells to patrol the protecting protecting of the mind.
To analyze how precisely CGRP influences the lymphatic system and contributes to migraine ache, the group of researchers carried out a plethora of experiments in vitro and in vivo. Nate Nelson-Maney, a MD-PhD scholar within the Caron lab and first writer on the paper, spearheaded these experiments.
Utilizing mouse fashions that had been resistant to the consequences of CGRP, they first confirmed that they skilled much less ache and spent extra time in a brightly lit chamber in contrast to people who had been susceptible to CGRP.
Brilliant gentle is a painful stimulus for individuals experiencing migraine, and the flexibility to measure related behaviors in mice validate the translational influence of the research.
Utilizing cell tradition methods, they assessed how a specialised protein is spatially organized between the person cells that line the lymphatic vessels. The protein, referred to as VE-Cadherin, helps maintain lymphatic endothelial cells caught collectively and controls how a lot fluid, like cerebrospinal fluid, can squeeze between lymphatic endothelial cells and go away the vessels.
Researchers discovered that lymphatic endothelial cells which have been handled with CGRP rearrange their VE-Cadherin proteins in order that they’re aligned like a zipper on a jacket, conserving a decent seal. This association prevents fluid from passing between cells, decreasing the permeability of those cell layers.
They validated this discovering in meningeal lymphatic tissue of mouse fashions handled with nitroglycerin-induced migraine. When CGRP and a traceable dye had been injected into the meningeal lymphatic vessels, they noticed a major discount within the quantity of cerebrospinal fluid exiting from the cranium.
Future research are wanted to disclose additional details about the prevailing relationships between migraine, CGRP, and meningeal lymphatic vessels. The analysis group will work to grasp how cerebrospinal fluid drainage by means of the meningeal lymphatic vessels contributes to migraine in people by means of research with and with out the usage of the newest FDA-approved CGRP-targeting drugs, corresponding to Nurtec, Emgality, Ajovy, and so forth.
Though CGRP has been recognized as the principle wrongdoer behind migraine-inducing adjustments to the lymphatic system, researchers don’t totally perceive the pathophysiology of migraine triggers and ache.
Extra analysis is required to grasp how meningeal lymphatic vasculature and the hormone-related life levels of ladies, corresponding to puberty, being pregnant, and menopause, play a task in producing migraine.
“Since lymphatic dysfunction additionally reveals a robust prevalence in girls, it’s tempting to invest that neurological issues like migraine could possibly be ruled by intercourse variations within the meningeal lymphatic vasculature,” mentioned Caron, who can be a member of the UNC Lineberger Complete Most cancers Middle.
“If this had been true, then new therapeutic methods or drug targets that improve meningeal lymphatic and glymphatic circulation in girls can be fascinating.”
About this migraine and neurology analysis information
Writer: Kendall Daniels
Supply: UNC
Contact: Kendall Daniels – UNC
Picture: The picture is credited to Neuroscience Information
Authentic Analysis: Open entry.
“Meningeal lymphatic CGRP signaling governs ache by way of cerebrospinal fluid efflux and neuroinflammation in migraine fashions” by Kathleen M. Caron et al. JCI
Summary
Meningeal lymphatic CGRP signaling governs ache by way of cerebrospinal fluid efflux and neuroinflammation in migraine fashions
Lately developed anti-migraine therapeutics focusing on calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) signaling are efficient, although their websites of exercise stay elusive. Notably, the lymphatic vasculature is attentive to CGRP signaling, however whether or not meningeal lymphatic vessels (MLVs) contribute to migraine pathophysiology is unknown.
Mice with lymphatic vasculature poor within the CGRP receptor (CalcrliLEC mice) handled with nitroglycerin (NTG)-mediated persistent migraine exhibit decreased ache and lightweight avoidance in comparison with NTG-treated littermate controls.
Gene expression profiles of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) remoted from the meninges of Rpl22HA/+;Lyve1Cre RiboTag mice handled with NTG revealed elevated MLV-immune interactions in comparison with cells from untreated mice.
Apparently, the relative abundance of mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (MAdCAM1)-interacting CD4+ T cells was elevated within the deep cervical lymph nodes of NTG-treated management mice however not in NTG-treated CalcrliLEC mice.
Therapy of cultured hLECs with CGRP peptide in vitro induced vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin rearrangement and decreased useful permeability.
Likewise, intra cisterna magna injection of CGRP prompted rearrangement of VE-Cadherin, decreased MLV uptake of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and impaired CSF drainage in management mice, however not in CalcrliLEC mice.
Collectively, these findings reveal a beforehand unrecognized position for lymphatics in persistent migraine, whereby CGRP signaling primes MLVs-immune interactions and reduces CSF efflux.













Discussion about this post