Spinal Cord Injury Diagnosis
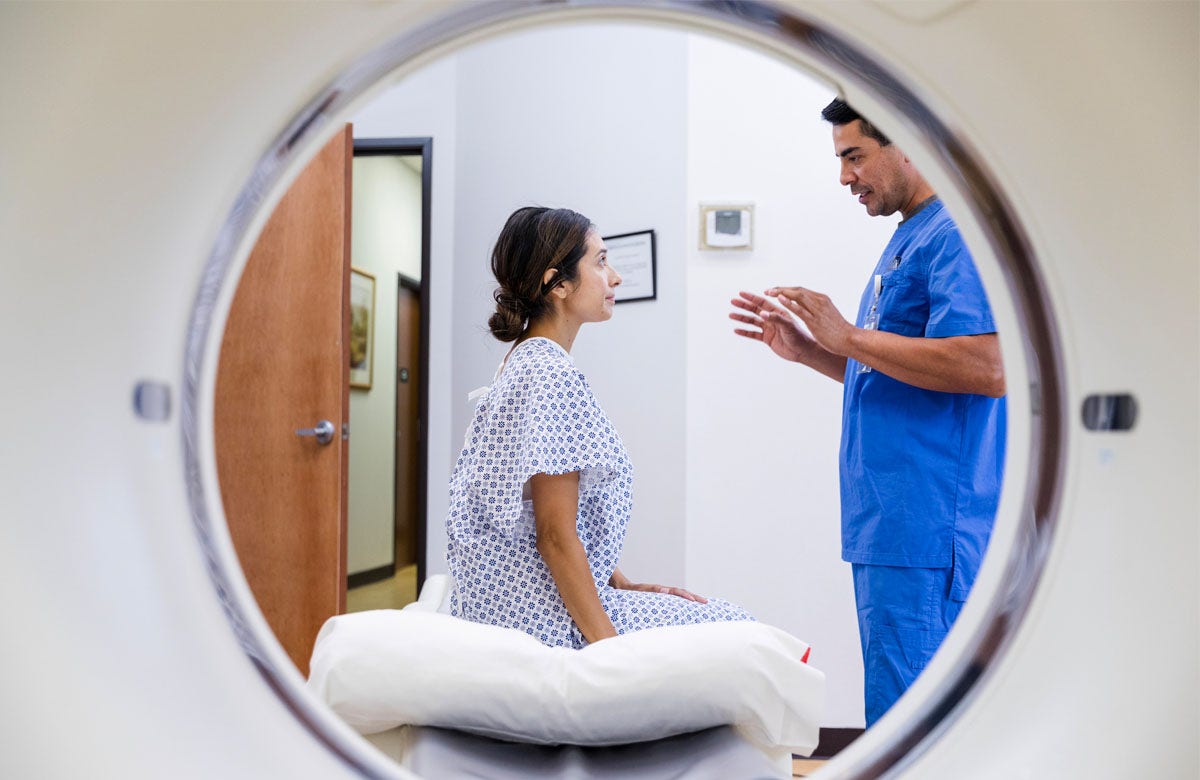
 In the emergency room, a doctor may be able to rule out a spinal cord injury by examination, testing for sensory function and movement, and by asking some questions about the accident. But if the injured person complains of neck pain, isn’t fully awake, or has obvious signs of weakness or neurological injury, emergency diagnostic tests may be needed.
In the emergency room, a doctor may be able to rule out a spinal cord injury by examination, testing for sensory function and movement, and by asking some questions about the accident. But if the injured person complains of neck pain, isn’t fully awake, or has obvious signs of weakness or neurological injury, emergency diagnostic tests may be needed.
These tests can include:
- X-rays. X-rays can reveal vertebral (spinal column) problems, tumors, fractures or degenerative changes in the spine.
- CT scan. A CT scan can provide a clearer image of abnormalities seen on X-ray. This scan uses computers to form a series of cross-sectional images that can define bone, disk and other problems.
- MRI. MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce computer-generated images. This test is helpful for looking at the spinal cord and identifying herniated disks, blood clots or other masses that might compress the spinal cord.
A few days after injury, when some of the swellings might have subsided, your doctor will conduct a more comprehensive neurological exam to determine the level and completeness of your injury. This involves testing your muscle strength and your ability to sense light touch and pinprick sensations.
Spinal Cord Injury Treatment
 Unfortunately, there’s no way to reverse damage to the spinal cord. But researchers are continually working on new treatments, including prostheses and medications, that might promote nerve cell regeneration or improve the function of the nerves that remain after a spinal cord injury. In the meantime, spinal cord injury treatment focuses on preventing further injury and empowering people with a spinal cord injury to return to an active and productive life.
Unfortunately, there’s no way to reverse damage to the spinal cord. But researchers are continually working on new treatments, including prostheses and medications, that might promote nerve cell regeneration or improve the function of the nerves that remain after a spinal cord injury. In the meantime, spinal cord injury treatment focuses on preventing further injury and empowering people with a spinal cord injury to return to an active and productive life.
Emergency Actions
Urgent medical attention is critical to minimize the effects of head or neck trauma. Therefore, treatment for a spinal cord injury often begins at the accident scene. Emergency personnel typically immobilize the spine as gently and quickly as possible using a rigid neck collar and a rigid carrying board, which they use during transport to the hospital.
Early (acute) Stages of Treatment
In the emergency room, doctors focus on:
- Maintaining your ability to breathe
- Preventing shock
- Immobilizing your neck to prevent further spinal cord damage
- Avoiding possible complications, such as stool or urine retention, respiratory or cardiovascular difficulty, and formation of deep vein blood clots in the extremities
If you have a spinal cord injury, you’ll usually be admitted to the intensive care unit for treatment. You might be transferred to a regional spine injury center that has a team of neurosurgeons, orthopedic surgeons, spinal cord medicine specialists, psychologists, nurses, therapists and social workers with expertise in spinal cord injury.
- Medications. Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) given through a vein in the arm (IV) has been used as a treatment option for an acute spinal cord injury in the past. But recent research has shown that the potential side effects, such as blood clots and pneumonia, from using this medication outweigh the benefits.Because of this, methylprednisolone is no longer recommended for routine use after a spinal cord injury.
- Immobilization. You might need traction to stabilize or align your spine. Options include soft neck collars and various braces.
- Surgery. Often surgery is necessary to remove fragments of bones, foreign objects, herniated disks or fractured vertebrae that appear to be compressing the spine. Surgery might also be needed to stabilize the spine to prevent future pain or deformity.
- Experimental treatments. Scientists are trying to figure out ways to stop cell death, control inflammation and promote nerve regeneration. For example, lowering body temperature significantly — a condition known as hypothermia — for 24 to 48 hours might help prevent damaging inflammation. More study is needed.
Ongoing Care
After the initial injury or condition stabilizes, doctors turn their attention to preventing secondary problems that may arise, such as deconditioning, muscle contractures, pressure ulcers, bowel and bladder issues, respiratory infections, and blood clots. The length of your hospital stay will depend on your condition and the medical issues you face. Once you’re well enough to participate in therapies and treatment, you might transfer to a rehabilitation facility.
Rehabilitation
 Rehabilitation team members will begin to work with you while you’re in the early stages of recovery. Your team might include a physical therapist, an occupational therapist, a rehabilitation nurse, a rehabilitation psychologist, a social worker, a dietitian, a recreation therapist, and a doctor who specializes in physical medicine (physiatrist) or spinal cord injuries. During the initial stages of rehabilitation, therapists usually emphasize maintaining and strengthening muscle function, redeveloping fine motor skills, and learning ways to adapt to do day-to-day tasks. You’ll be educated on the effects of a spinal cord injury and how to prevent complications, and you’ll be given advice on rebuilding your life and increasing your quality of life and independence. You’ll be taught many new skills, and you’ll use equipment and technologies that can help you live on your own as much as possible. You’ll be encouraged to resume your favorite hobbies, participate in social and fitness activities, and return to school or the workplace.
Rehabilitation team members will begin to work with you while you’re in the early stages of recovery. Your team might include a physical therapist, an occupational therapist, a rehabilitation nurse, a rehabilitation psychologist, a social worker, a dietitian, a recreation therapist, and a doctor who specializes in physical medicine (physiatrist) or spinal cord injuries. During the initial stages of rehabilitation, therapists usually emphasize maintaining and strengthening muscle function, redeveloping fine motor skills, and learning ways to adapt to do day-to-day tasks. You’ll be educated on the effects of a spinal cord injury and how to prevent complications, and you’ll be given advice on rebuilding your life and increasing your quality of life and independence. You’ll be taught many new skills, and you’ll use equipment and technologies that can help you live on your own as much as possible. You’ll be encouraged to resume your favorite hobbies, participate in social and fitness activities, and return to school or the workplace.
Medications
Medications might be used to manage some of the effects of spinal cord injury. These include medications to control pain and muscle spasticity, as well as medications that can improve bladder control, bowel control and sexual functioning.
New Technologies
Inventive medical devices can help people with a spinal cord injury become more independent and more mobile. These include:
- Modern wheelchairs. Improved, lighter weight wheelchairs are making people with spinal cord injuries more mobile and more comfortable. Some people need an electric wheelchair. Some wheelchairs can even climb stairs, travel over rough ground and elevate a user to reach high places without help.
- Computer adaptations. For someone who has limited hand function, computers can be difficult to operate. Computer adaptations range from simple to complex, such as key guards and voice recognition.
- Electronic aids to daily living. Essentially any device that uses electricity can be controlled with an electronic aid to daily living. Devices can be turned on or off by switch or voice-controlled and computer-based remotes.
- Electrical stimulation devices. Often called functional electrical stimulation systems, these sophisticated devices use electrical stimulators to control arm and leg muscles to allow people with spinal cord injuries to stand, walk, reach and grip.